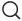Illustrated in the slide is the surgical resection of a cerebral carcinoma, originating from different cells within the central nervous system (CNS).
Adult brain tumors have a one-third chance of malignancy and constitute approximately 2% of all cancers in the United States. Malignant brain tumors can originate from CNS tissue or, more commonly, they can stem from malignancies in other organ systems.
Clinically, brain tumors are manifested by symptoms such as increased intracranial pressure (ICP), headaches, seizures, syncope, and cognitive impairment.
The diagnostic approach focuses on gathering a detailed patient history, performing a comprehensive neurologic examination, and obtaining neurologic imaging studies to gain a thorough understanding of the tumor’s characteristics.
The treatment strategy depends on accurately grading/staging the tumor and defining its origin. Therapeutic interventions include surgical interventions, chemotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, immunotherapy, and whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT).
This comprehensive approach facilitates navigation of the complexities of brain tumor management.
Categories
Adult Brain Tumors: A Spreading Problem
Adult Brain Tumors: A Spreading Problem
 March 5, 2024
March 5, 2024  By admin
By admin